Instrumentation
UIW's Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry offers students a wide array of instruments with which to work and learn. These high-performance instruments form a critical part of chemistry and biochemistry education, as students use them to observe, experiment, analyze, and continually improve their methods.
Reservation of instrument time is done online using the Clustermarket software.
Spectroscopy
NMR Spectrometers
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a non-invasive and non-destructive analytical technique used in chemistry that can be used to determine the structural identity, purity, reaction dynamics, or molar ratio of organic products, such as small organic molecules or protein structures. Making use of a unique phenomenon that occurs when a sample is placed in a static magnetic field and subjected to an oscillating electromagnetic field, causing a small population of nuclei to resonate. NMR is fundamental to all research that involves small organic molecules, such as pharmaceutics, chemical biology, biophysics, ligand development in inorganic research, and is heavily used in research labs globally, in both academia and in industry. The medical correlate of NMR is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is a multidimensional NMR imaging technique used to observe matter at the macroscopic scale.

Bruker 300 MHz Avance III HD.
Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy
The light produced after a sample is excited with a plasma can be used to determine the concentration of specific elements through inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. This technique is used in research labs specializing in pharmaceutical, environmental, and chemical analysis.

Agilent 5110 ICP-OES.
Spectrofluorometer
Fluorescence spectrometry is a technique that measures the light emitted by a sample. Spectrofluorometers can be used to detect compounds that fluoresce and are at very low concentrations such as impurities in pharmaceuticals. This technique is also used to characterize new compounds which have applications in the pharmaceutical and medical fields.
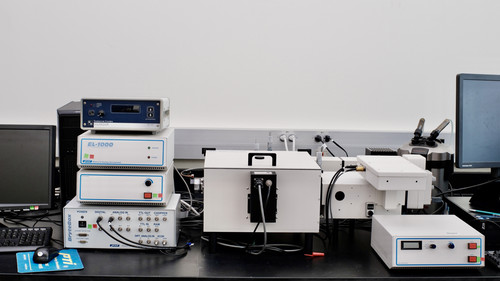
PTI Quantamaster 4 with lifetime capability.
UV-Vis Spectrophotometer
UV-vis is an analytical technique that quantitatively measures the amount of light that is absorbed by a chemical substance. As light of a given intensity passes through a sample, some of that light is absorbed or reflected by the sample, and so a measurement of the difference between the sample and a reference sample is obtained. These absorption-transmission measurements are used to determine the concentration of a substance, or the kinetics of a chemical reaction. UV-vis is used in standard chemistry research, biochemistry, microbiology, material science, petrochemistry, food science, pharmaceutics, and quality control settings.
UV-Vis training is initiated online through the following link:

Agilent Cary 8454.
Infrared Spectrometer
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is a robust analytical technique used to obtain high spectral resolution data over a wide spectral range by measuring infrared intensity against wavelength of light. By passing IR light through a sample and measuring how much light is absorbed by chemical bonds through stretching and vibrating, a researcher is able to collect a molecular fingerprint of a compound’s functional groups. FTIR is used widely in academic research in organic synthesis, polymer chemistry, quality control, forensic analysis, biological research, and in the pharmaceutical industry.
IR training is initiated online through the following link:

Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS20 FTIR Spectrometer.
Chromatography
High-Performance Liquid Chromatograph
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful technique used broadly in the majority of chemistry and biochemistry research settings, in both academia and in industry. HPLC is used when there is a need to separate analytes based on molecular structure or composition. Using mobile and stationary phases, and a pump rather than gravity, it can be used for quantifying, purifying, and identification of analytes in a mixture. Multiple detectors may be used in HPLC, thereby making this technique all the more robust. Our HPLC is equipped with detection by UV/Vis, fluorescence, and by mass spectrometry. The advantages of HPLC as a chromatographic technique are speed, accuracy, and efficiency. Typical applications include the fields of forensics, pharmaceutics, environmental studies, clinical testing, and food science.

Agilent Infinity 1260 HPLC
Gas Chromatograph/Mass Spectrometer
Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer (GC-MS) is a very robust instrument that combines two powerful techniques. The GC separates volatile and thermally stable substances in a sample, while MS fragments the analyte based on its mass and therefore identified. Given the power of separation, high sensitivity and wide range of detectable analytes, and quick turn-around of results, GC-MS is a widely used technique. GC-MS is used in medicine for the detection of several congenital metabolic diseases, for monitoring the environment, in food science, pharmaceutical industry at all stages of production and characterization, in forensic toxicology and anti-doping labs, and has been used to analyze the atmospheres of Venus and Mars.

Agilent 7820A GC-MS
Preparation
Glove Box

MBraun Lab Master SP.
Microwave Acid Digestion

CEM MarsXpress 230/60.
Microwave Synthesizer

CEM Discover SP.
Pricing for instrument use can be found below
Contact us at cbic@uiwtx.edu with any questions.
